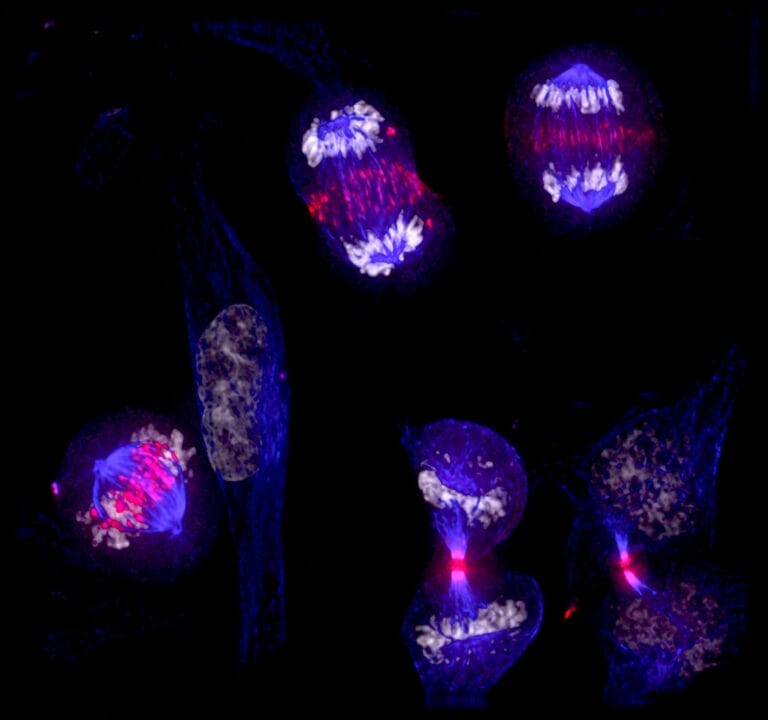
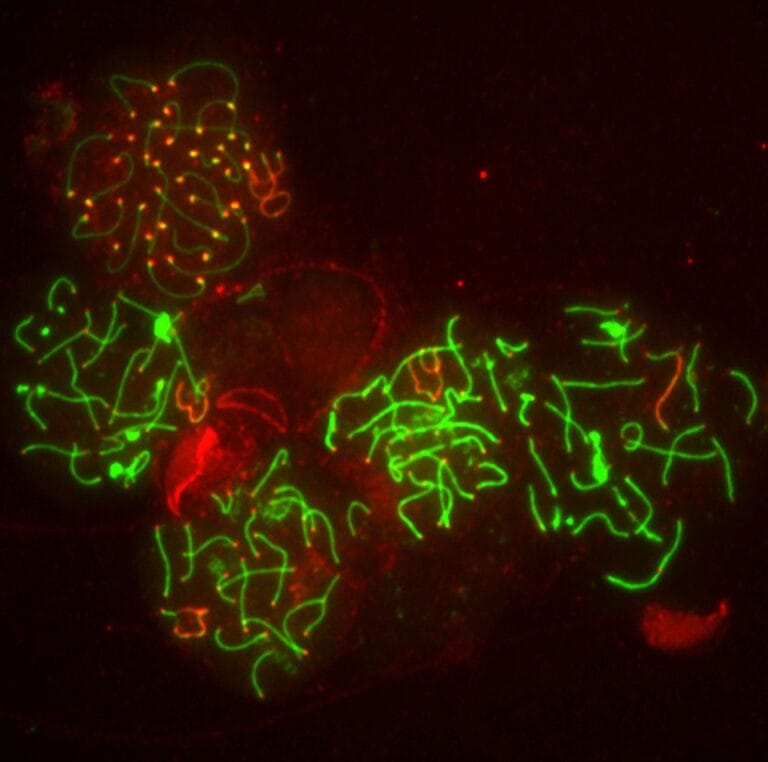
Mitosis versus meiosis
Image credit: Laura Trinkle-Mulcahy / Wellcome Collection.
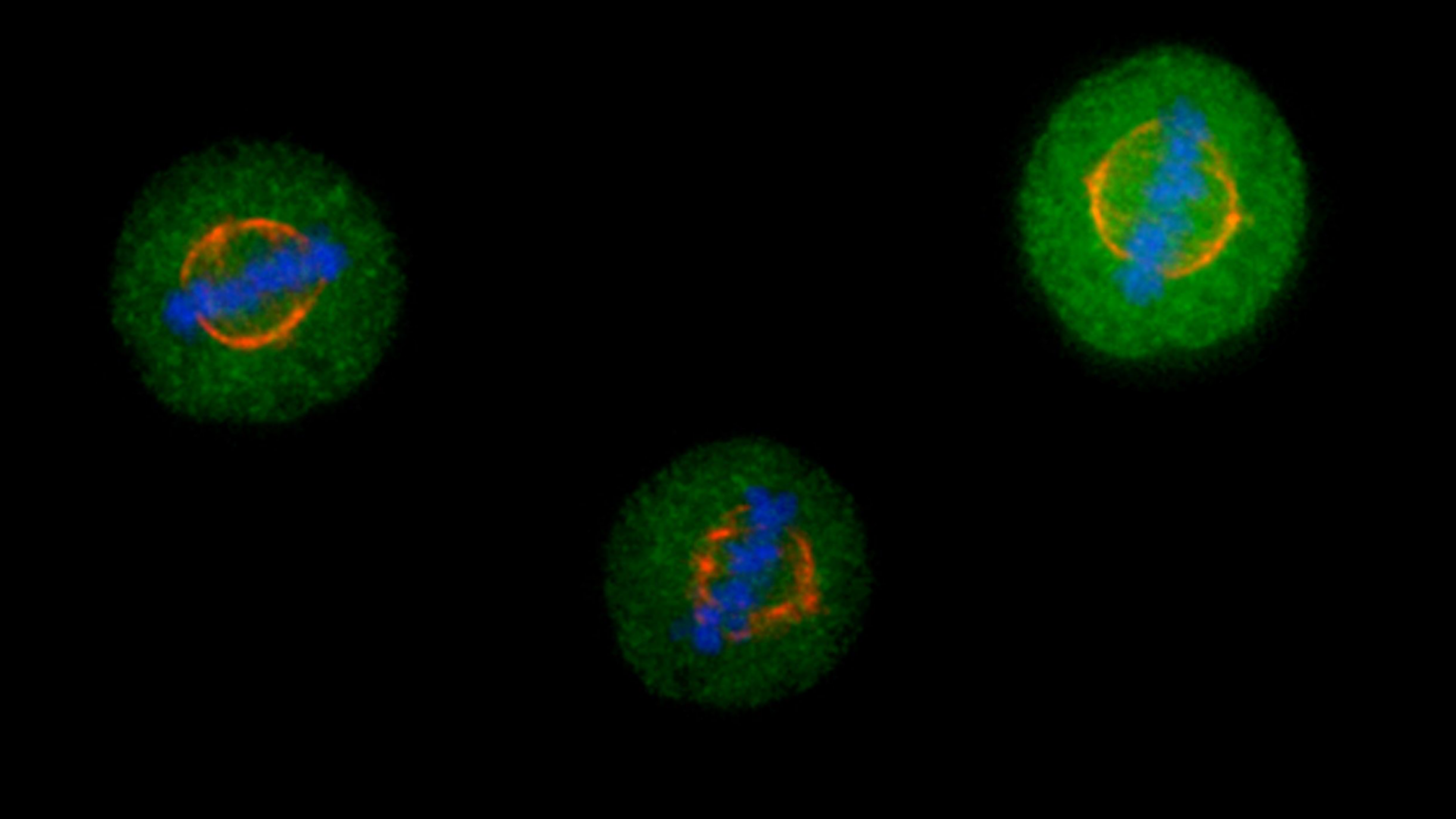
Cells divide and reproduce in two ways, mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis results in two identical daughter cells, whereas meiosis results in four sex cells. Below we highlight the key differences and similarities between the two types of cell division.
Differences and similarities between mitosis and meiosis
What are the similarities?
Both mitosis and meiosis involve:
- Diploid parent cell
- Stages of interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase
- In metaphase individual chromosomes (pairs of chromatids) line up along the equator
- During anaphase the sister chromatids are separated to opposite poles
- Ends with cytokinesis
What are the differences?
| Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|
| Involves one cell division | Involves two successive cell divisions |
| Results in two daughter cells | Results in four daughter cells |
| Results in diploid daughter cells (chromosome number remains the same as parent cell) | Results in haploid daughter cells (chromosome number is halved from the parent cell) |
| Daughter cells are genetically identical | Daughter cells are genetically different |
| Occurs in all organisms except viruses | Occurs only in animals, plants and fungi |
| Creates all body cells (somatic) apart from the germ cells (eggs and sperm) | Creates germ cells (eggs and sperm) only |
| Prophase is much shorter | Prophase I takes much longer |
| No recombination/crossing over occurs in prophase. | Involves recombination/crossing over of chromosomes in prophase I |
| In metaphase individual chromosomes (pairs of chromatids) line up along the equator | In metaphase I pairs of chromosomes line up along the equator |
| During anaphase the sister chromatids are separated to opposite poles | During anaphase I the sister chromatids move together to the same pole; During anaphase II the sister chromatids are separated to opposite poles |