What are dominant and recessive alleles?
Image credit: Shutterstock
Different versions of a gene are called alleles. Alleles are described as either dominant or recessive depending on their associated traits.
- Most human cells carry two copies of each chromosome, so usually have two versions of each gene.
- These different versions of a gene are called alleles.
- Alleles can either be dominant or recessive, which describes the way their associated traits are inherited.
What are dominant and recessive alleles?
- Since most human cells carry two copies of each chromosome, they have two versions of each gene – with one inherited from each parent.
- These different versions of a gene are called alleles. An individual might have two of the same alleles (known as being homozygous) or two different alleles (known as being heterozygous).
- Alleles can be either dominant or recessive.
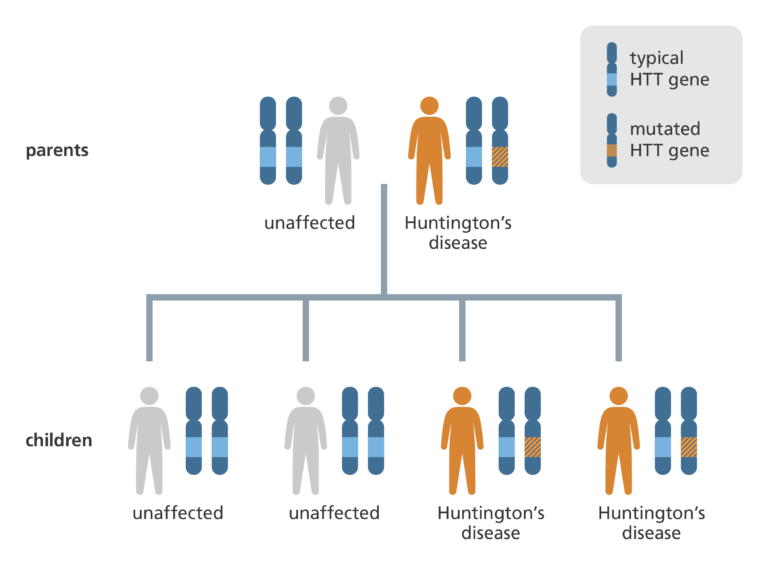
- Dominant alleles can influence a specific trait if a person has one or both copies of the allele, which can come from just one or both parents.
- For example, Huntington’s disease is a dominant condition caused by an insertion mutation in the HD (sometimes called HTT) gene. Individuals only need to inherit one mutated copy of the gene to experience symptoms.
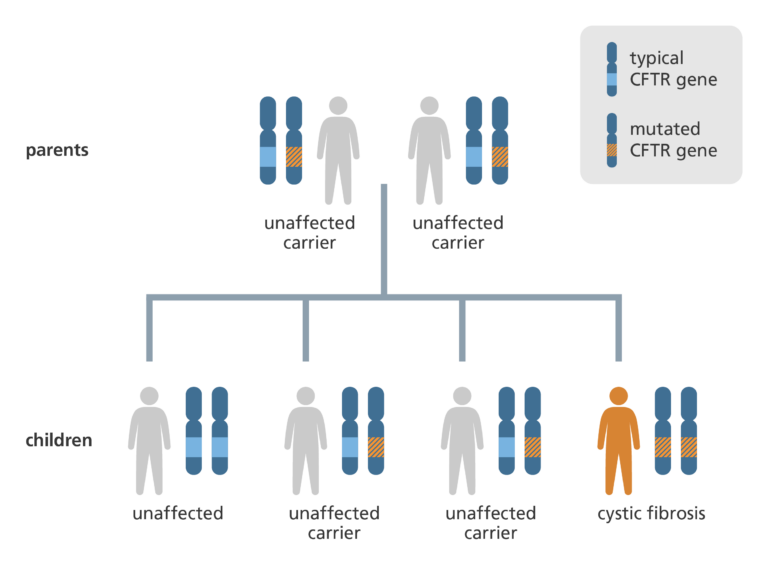
- Recessive alleles only show their effect if the individual inherits two copies of the allele – one from each parent. If an individual has only one copy of the recessive allele, they are generally considered to be a ‘carrier’ of the recessive allele.
- For example, cystic fibrosis is a recessive condition caused by a mutation in the CFTR gene. That means a person needs a mutation in both CFTR alleles to have cystic fibrosis. If an individual has a mutation in one CFTR allele but not the other, they are a carrier of cystic fibrosis, but won’t develop the condition themselves.
- If both alleles are dominant, it’s called codominance. The resulting characteristic is due to both alleles being expressed equally. For example, the blood group AB which is the result of codominance of the A and B dominant alleles.
- For a long time, scientists thought that most of our traits are inherited in this dominant / recessive relationship, known as Mendelian inheritance. However, we now know that many of our traits are controlled by multiple genes and other factors in a more complex way than this simple model of inheritance.
What are sex-linked genes?
- As we introduced on our ‘What is inheritance’ page, a person’s sex traits – such as their genitalia, hormones, reproductive organs – are determined by the sex chromosomes. These are chromosomes X and Y.
- Genes found on the X and Y chromosomes are called sex-linked genes. Chromosome Y is smaller than chromosome X and doesn’t have all the genes that are found on chromosome Y.
- That means that while people with the XX genotype have two copies of each gene, people with the XY genotype only have one copy of some sex-linked genes.
- Some genetic conditions are caused by sex linked genes. For example, haemophilia is a recessive sex-linked condition.
- People with XX chromosomes need to have two copies of the haemophilia allele to develop the condition.
- However, because people with XY chromosomes only have one copy of the haemophilia gene, they only need one copy of the haemophilia allele to develop the condition.
- This means haemophilia is much more common in people with XY chromosomes than people with XX chromosomes.